This article explains, in plain language, the U.S. patent that underpins SEO Vendor’s CORE AI. It’s meant to help practitioners and clients understand what is actually protected, what problems it addresses, and where its limits are.
Table of Contents
Quick summary
- Patent title & number: Website Analyzing Method, US 12,093,650 B2 (granted Sept. 17, 2024).
- The patent describes an “AI analysis unit” with multiple AIs: a language AI, trend-predicting AI, and competition analyzer AI. These handle NLP categorization, trend prediction from ranking data, and competitive comparisons, and they generate scores/alerts used in the workflow. (Google Patents)
- Strategy idea: Analyze a website’s keyword and anchor-text usage (and related signals) against strategy-defined boundaries, compute health scores, and warn users before optimization drifts into risky patterns that could be treated as “black-hat” by search engines. (Google Patents)
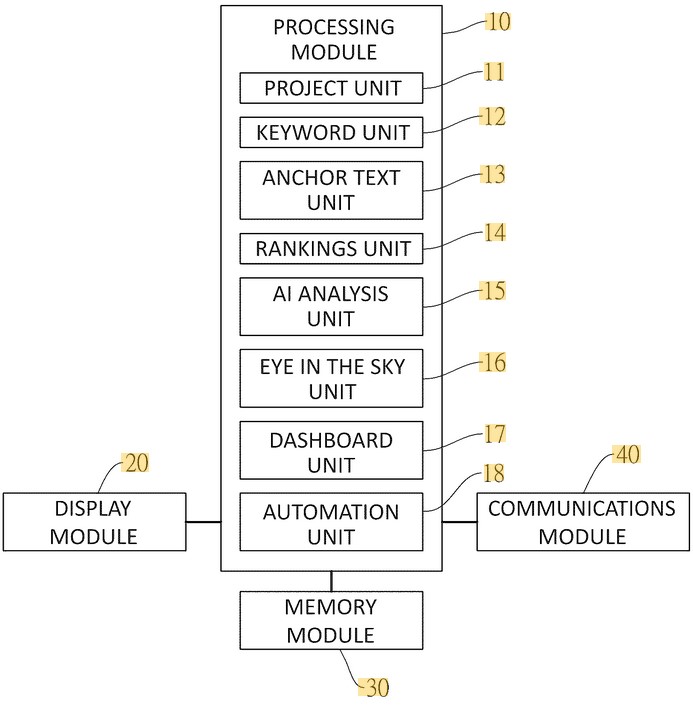
- System shape: A processing module connected to units for project, keyword, anchor text, rankings, AI analysis, “Eye in the Sky,” dashboard, automation, plus display, memory, and communications.
The problem the patent is trying to solve
Search engines behave like black boxes. Traditional SEO tools may push aggressive keyword/anchor changes without tracking boundaries, increasing the risk of spammy patterns. The patent frames this as a need for guardrails so optimizations are tracked and stay in a “white-hat” zone rather than drifting into tactics that search engines could penalize. (Google Patents)
What the patent claims at a high level
While the formal claims are legal language, the invention, when boiled down, covers a method that:
- Loads a website project and counts words/keywords relevant to anchor-text types.
- Computes internal percentages (e.g., exact-match, partial-match, branded, URL, etc.).
- Loads default percentages from a chosen strategy (the “protection boundary”).
- Compares actual vs. default; when a threshold is exceeded, marks and warns.
- Displays the percentages and warnings; may score health, trigger alerts, and guide next steps.
You’ll also see flows and UI states that visualize anchor-type targets vs. actuals (e.g., charts/tables for “optimal %” vs. “actual %”), and steps for health scoring and notifications.
How the system is organized
The patent’s block diagram contains modules commonly found in analytics platforms, but combined in a particular way for this method:
- Processing module orchestrates the method.
- Project, Keyword, Anchor-Text, Rankings units handle inputs and tracking.
- AI Analysis unit supports analysis logic.
- “Eye in the Sky” unit monitors conditions.
- Dashboard & Automation units surface insights and can trigger comms/alerts.
- Display/Memory/Communications modules handle UI, storage, and external data/tools.
The workflow, step by step (plain English)
- Ingest & classify: Pull in the site/project; classify anchors/keywords into types.
- Set boundaries: Load a strategy with default anchor-type percentages (the safe zone).
- Measure reality: Compute the actual percentages from current content/links.
- Compare & warn: If actuals exceed strategy boundaries, flag the risky types and generate warnings (e.g., “branded anchors too low,” “exact-match too high”).
- Score health: Aggregate signals into a health score; if low, highlight as unhealthy and send alerts (e.g., email).
- Guide changes: Provide a dashboard and, optionally, keyword customization windows for corrective action.
How AI Fits Into the Method (and where Neural Networks Come In)
The patent’s workflow isn’t just counting words—it’s driven by an AI analysis unit that classifies language, watches ranking trends, compares competitors, and turns those signals into scores and warnings the dashboard can act on. (Google Patents)
What the patent names, specifically:
- A language AI that helps categorize keywords and can assign word scores (useful for mapping and prioritization). It contributes to alerts when scores drop below thresholds. (Google Patents)
- A trend-predicting AI that looks at rank fluctuations over time and produces a trend signal for each cycle, feeding the project’s health status. (Google Patents)
- A competition analyzer AI that compares your keywords to ranked URLs and builds competitive context, which informs recommended link-type mixes and other tactical choices. (Google Patents)
Why this matters:
These AIs are how the system learns from real data instead of relying only on static rules. They’re the bridge between raw metrics (anchor text counts, ranking deltas) and actionable guidance (health scores, boundary warnings, recommendations).
About neural networks (ANNs):
The patent claims the method and system—it doesn’t require a particular model architecture. In practice, CORE AI is described publicly as using an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) framework to learn from many factors (on-page, off-page, historical behavior). Think of this as the engine that helps the analysis unit generalize patterns and adapt faster; the patent covers what the engine does, while ANN is how your implementation powers it. (SEO Vendor)
What makes this approach different
- Explicit “protection boundaries.” Rather than optimizing blindly, the method enforces strategy-defined limits for anchor usage—intended to reduce the chance of algorithmic penalties. (Google Patents)
- Integrated scoring and alerts. It doesn’t just measure; it scores health and can notify stakeholders when thresholds are breached.
- Visualization of target vs. actual. Figures show side-by-side charts/tables for optimal vs. real anchor distributions to guide adjustments.
- The AI analysis unit is central to the patented method: it categorizes, predicts, compares, scores, and triggers alerts that keep optimization inside the safe zone. (Google Patents)
- Neural networks aren’t spelled out in the patent text, but they’re the documented implementation behind CORE AI’s learning behavior. (SEO Vendor)
How this maps to CORE AI (the product family)
CORE AI’s page describes an ANN-based system with “Eye in the Sky” monitoring and branch-prediction style analysis, emphasizing proactive detection of risky patterns and faster adaptation to algorithm changes.
The patent’s guardrail and monitoring workflow underpins this capability, tracking anchor/keyword usage, computing health, and issuing warnings that the CORE AI dashboard surfaces. (SEO Vendor)
- “Eye in the Sky” (EITS): The patent’s monitoring and alerting steps align with CORE AI’s promise to watch for changes and surface health issues.
- Strategy boundaries ≈ “safe zone”: The site explicitly notes CORE AI “creates a protection boundary… to remain the ‘safe zone’,” which reflects the patent’s boundary-comparison logic. (SEO Vendor)
Bottom line: the legal protection is on the method of analyzing and constraining optimization behavior via strategy boundaries, health scoring, and warnings—implemented within the system architecture shown in the figures.
Practical implications for marketers and site owners
- Operational guardrails: Teams can pursue growth while staying inside guard rails for anchor usage—lowering the risk of over-optimization. (Google Patents)
- Faster triage: Health scores and alerts help catch problems early (e.g., anchor drift after a campaign or content migration).
- Clearer communication: Visual “optimal vs. actual” views make it easier to explain why certain changes are needed.
What the patent does not claim
- It doesn’t claim to predict search rankings with certainty, nor to describe Google’s internal algorithms.
- It doesn’t claim ownership of all SEO analytics; rather, it protects this specific method of boundary-based analysis, health scoring, and warning flows applied to keyword/anchor usage within a defined system.
FAQs
Is this only about links and anchors?
Anchors and keyword usage are central, but the system also references rankings and analysis units that can incorporate multiple factors as part of health scoring and decision support.
How does it relate to CORE AI’s “ANN” and “EITS”?
The patent sets out the method and system structure; the product pages describe implementation choices (ANN, continuous monitoring) that realize those claims in practice. (SEO Vendor)
Why does this matter now?
As search becomes more sensitive to manipulative patterns, having methodical boundaries and auditable warnings helps keep long-term risk low while you iterate on strategy. (Google Patents)
Source materials
- U.S. Patent No. 12,093,650 B2, “Website Analyzing Method,” figures, abstract, and specification.
- CORE AI overview page (product descriptions, ANN/EITS concepts, and “safe zone” language). (SEO Vendor)